[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]To depreciate a business asset and complete IRS Form 4562
Depreciation and Amortization, there are few things to consider:
- Which depreciation to use
GDS
ADS
- Property class
You need to know in which category
your asset is.
- Recovery Period
It is usually equal to the property class
if your asset is listed or included in the basic ones.
In general:
office machines like calculators are 5-years
property class with 5 yrs. recovery periods.
Office furniture
are 7 years property class with 7 years recovery period.
Residential rental
properties like single house and apartments have 27.5 recovery periods.
Non-residential
properties like commercial building and warehouses have 39 years of recovery
periods.
Your house office
in your house if depreciated, has 39 years of recovery period like
nonresidential property.
Home office in
your apartment in your apartment building you own, if depreciated has 27.5
years of recovery period as residential property.
- Date you place your property is service.
It is when it is available and ready to be
used even if it was not used right away.
- Business use
It is 100% if you use it for business only.
If you use it for both personal and
business, you need to track the usage.
If you use it for both investment and
business, you need to track the usage.
- Depreciation convention
Mid-month convention
Use it for
residential and non-residential properties.
Mid-quarter Convention
Use this convention
if properties placed in service and disposed of during the last 3 months of the
year is more than 40% all the basis of the properties you acquired and placed
in service that year not included residential and nonresidential properties.
In this convention,
you place properties in service and dispose of them halfway in the quarter you
placed them in service or disposed of them.
You need to know the
quarter in which you placed each property in service.
Half-Year Convention
This convention treats
the properties you placed in service during the year as placed in service halfway
through the year.
Use it if mid-month
convention and mid-quarter convention do not apply to you.
- Depreciation methods
- 200% declining method under GDS
- 150% declining method under GDS
- Straight line method under GDS
- Straight line methods under ADS
To calculate your depreciation deduction for properties you placed in
service during the year, you need to know:
- Date placed in service
- Basis amount
- Depreciation system (GDS, ADS)
- Property class
- Recovery period
- Convention method (MM, MQ, HY)
- Depreciation method (200% GDS, 150% GDS, SL GDS,
SL ADS) - Locate IRS depreciation rate table or calculate
it yourself.
To depreciate an asset, you usually use GDS. You do not use
ADS unless you are required to or elect to.
One example you are required to use ADS is when you use a
listed property for 50% or less in your business and the rest for investment or
personal. You would use investment and business uses % in the depreciation
deduction calculation but use business % to figure out whether ADS is required
or not.
Appendix A on IRS Publication 946 How to Depreciate Property
Depreciation rate table from IRS Publication 946
Appendix B Table of Class Lives and Recovery Periods – IRS
Publication 946
How to use Appendix B?
Appendix B is helpful to determine both the class lives and
recovery periods for your depreciable assets.
Option 1
You need to look at both table B-1 and table B-2 to use the
correct recovery period.
Look for your depreciable asset in table B-1.
If you find it, go to table B-2 to locate the business
activity that uses it.
If you find the business activity, see if the asset been
depreciated is listed in the list under that activity.
If you see the asset, use the recovery period listed in
table B-2 for that asset class.
Option 2
If you find the property described in Table B-1 and go to
table B-2 but do not see the business activity or you see the business activity,
but the asset is not listed in the list under that type of business activity,
go back to table B-1 to look for the asset again and use the recovery period
listed in table B-1.
Option 3—Asset is not in Table B-1, Business activity is in Table B-2, &
Asset is listed in Table B-2 under the business activity
If the asset is not in table B-1, look for the activity in
table B-2 and look for the assets listed there. If your asset is listed, use
the recovery period in table B-2 for that asset class.
Option 4: Asset is not in Table B-1, Business activity is in Table B-2, but
Asset is not specifically listed under that business activity in table B-2
If the asset is not listed in table B-1, go to table B-2 to
look for the business activity that uses it. If you find the business activity,
read its description for assets listed. If the asset is not specifically listed
under that business activity, use the recovery period in table B-2 for that
business activity asset class.
Option 5
If the asset been depreciated or the business activity that
uses is not listed in table B1 and table B-2, go to the end of table B-2 for
recovery period assigned for certain property.
Example. Printer is listed in table B-1 0.12 asset class.
Table B-2 as the business in asset class 57.0 but printer is
not listed there. Therefore, recovery period in table B-1 for asset class
00.12, 5 years would be used. It is a 6-year class life asset. It is a 5-year
property class with a recovery period of 5 years under GDS.
Now that you know the asset class, the recovery period, go
to Appendix A table to decide for the depreciation MACRS system you want to use
which depreciation method based on your recovery period, you would use knowing
the convention, class, date placed in service and find the depreciation rate
table. In our printer example:
MACRS System: GDS
Depreciation Method: SL
Recovery Period: GDS/5
Convention: HY
Asset Class life: 6
Property class: 5
Quarter placed in service: Any
Table: A-8
Example 2: Vinyl cutter not listed in Appendix B
Table B-1
Vinyl cutter
It is not listed in table B-1
Table B-2 listed asset class 57 retail trade the business
activity.
The description of assets under the business activity didn’t
specifically specify vinyl cutter.
The class life and recovery period under asset class 57.0
would be used for the vinyl cutter depreciation.
Class life: 9
Recovery period: 5 under GDS
Now you would go to Appendix A to find the remaining
criteria that would guide into locating the rate table to use to depreciate it.
How to find the property class?
Find the class life in years using table B-1 and B-2. Take
note of the class life in years.
Locate the classification chart on IRS Instructions for Form
4562 Depreciation and amortization page 8 (for 2021 form). Use the chart to
match the class life in years to the property class. For instance, an asset
with class life in years ranging between 4-10 years (4- and 10-years class life
assets are not included) is a 5-year property.
If you don’t know the recovery period, there is a chart in
the same instruction page 9 that corresponds each property class to its
recovery period. Generally, you could locate the recovery period in Appendix B
Table B-1 and B-2 of Publication 946.
Summary
You need to know your asset class life in years, its
property class, its recovery period, the type of MACRS to use, the time it is
placed in service to locate the right depreciation table number in Appendix A
of IRS Publication 946.
1-How to Depreciate Business Assets
The video explains the process.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1652095686754{margin-top: 10px !important;margin-bottom: 10px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_video link=”https://youtu.be/5hEhPMBpRgg” el_width=”60″ el_aspect=”43″][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1652095686754{margin-top: 10px !important;margin-bottom: 10px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_cta h2=”How do You Depreciate a Business Asset?” h2_font_container=”color:%23000000″ h2_google_fonts=”font_family:Spirax%3Aregular|font_style:400%20regular%3A400%3Anormal” h4=”Articles and videos to assist you claim the right depreciation deduction on your business assets.” h4_font_container=”color:%23000000″ h4_google_fonts=”font_family:Tauri%3Aregular|font_style:400%20regular%3A400%3Anormal” style=”custom” add_button=”right” btn_title=”Previous Articles” btn_style=”custom” btn_custom_background=”#5bc98c” btn_custom_text=”#000000″ use_custom_fonts_h2=”true” use_custom_fonts_h4=”true” h2_link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fninasoap.com%2Fcategories%2Fhow-do-you-depreciate-a-business-asset%2F|title:How%20do%20You%20Depreciate%20a%20Business%20Asset||” h4_link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fninasoap.com%2Fcategories%2Fhow-do-you-depreciate-a-business-asset%2F|title:How%20do%20You%20Depreciate%20a%20Business%20Asset||” custom_background=”#d5e8f2″ custom_text=”#000000″ btn_link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fninasoap.com%2Fcategories%2Fhow-do-you-depreciate-a-business-asset%2F|title:How%20do%20You%20Depreciate%20a%20Business%20Asset||”][/vc_cta][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1652095686754{margin-top: 10px !important;margin-bottom: 10px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1652095686754{margin-top: 10px !important;margin-bottom: 10px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_wp_text title=”Welcome to Digital download store!”]
Digital templates and spreadsheets to assist you manage your money, your business, and file your business taxes without stress.
Business Consulting Session:
Weekly business virtual meeting to assist Sole Proprietor, LLC, and S Corporation owners with business and tax related issues.
Small Business Group Session-Quarter 1:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/small-business-group-session-quarter-1/
Small Business Group Session-Quarter 2:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/small-business-group-session-quarter-2/
Small Business Group Session-Quarter 3:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/small-business-group-session-quarter-3/
Small Business Group Session-Quarter 4:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/small-business-group-session-quarter-4/
How to manage your business:
Business Planners and templates to help you manage your business successfully, file your business taxes and claim the right deductions.
Business Expense Excel Spreadsheet-LLC-BEESL31321:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/business-expense-excel-spreadsheet-llc-beesl31321/
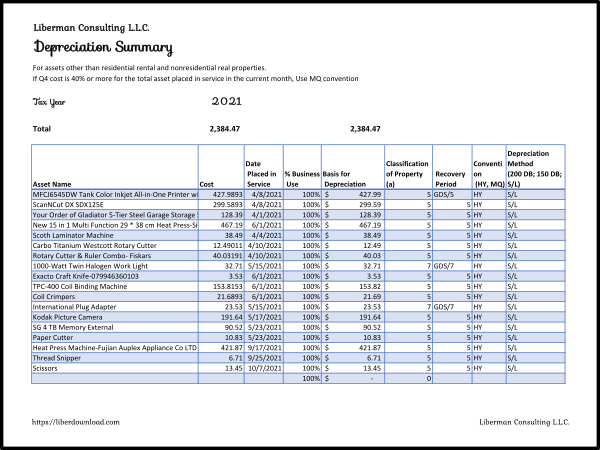
Depreciation Worksheet PDF-DWP21121:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/depreciation-worksheet-pdf-dwp21121/
Depreciation Summary Spreadsheet-DSS22821:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/depreciation-summary-spreadsheet-dss22821/
Depreciation Spreadsheet-DS22821:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/depreciation-spreadsheet-ds22821/
Daily To Do List PDF – DTDLP1221:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/daily-to-do-list-pdf-dtdlp1221/
Daily To Do List PDF – DTDLPBW1221:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/daily-to-do-list-pdf-dtdlpbw1221/
Daily Work Activity Log Excel Template – DWALET21221:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/daily-work-activity-log-excel-template-dwalet1121/
Form 940 Business Tax Checklist – F94011821:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/form-940-business-tax-checklist-f94011821/
Form 944 Business Tax Checklist – F94411821:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/form-944-business-tax-checklist-f94411821/
How to manage your money:
Finance Planners to manage your money, pay off your debts, and put your money to work.
Budget and Monthly Expense Tracker – BO2D22:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/budget-and-monthly-expense-tracker-bo2d22/
For more digital products would you please visit: https://liberdoanload.com.
For printed business stationery ready to ship to your door: https://liberlabel.com
[/vc_wp_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1652095686754{margin-top: 10px !important;margin-bottom: 10px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_wp_text]
Disclaimer:
“I am not an attorney to practice law. I am not allowed to draft legal documents, give advice on legal matters including immigration, or charge a fee for these activities.” Our articles are informative and based on our knowledge and experience. They are for educational purpose only. Use them at your own discretion.
Affiliate Links Disclaimer:
Our articles contain affiliate links. When you click on one of our affiliate links and make a purchase, we will receive a commission. We thank you very much for your support!
Please Find About our Products and Links Below
Free Download
Would you please check the “Free Download” section on our website for budget spreadsheet, budget planner PDF, tax forms, motivational quotes, checklists, and more for you do download. You don’t need to subscribe to access them. We would like to have you in our community where we interact and encourage each other to reach our goals. We invite you to join our email list, but it is not required to download from Free downloads.
https://ninasoap.com/free-downloads/
Our Objectives
At Nina’s Soap (Liberman Consulting L.L.C.), you would find information to live a quality life within budget and increase your net worth. Topics covered include personal finance, investment, business management, cooking from scratch and growing some vegetables and fruit to save money and eat healthy.
For more, would you please check our blog:
Contact Information: care@ninasoap.com
You Tube Channel:
Are you a visual type person? We got you covered! You can watch video contents including how to file your business tax returns yourself at:
https://www.youtube.com/c/LibermanConsultingLLC
Liberman Consulting L.L.C. Podcast:
Do you like to listen to podcast while you are busy working to maximize your time and learn at the same time? You can listen to contents including how to save money and create multiple sources of income at:
https://www.buzzsprout.com/1585738/
Join Us for Free
You are invited to join us where you could ask questions, stay motivated and work toward reaching your financial goals.
How to Find Previous Articles
To make it easy to navigate our website, would you please check the side bar? Under “Post Archives”, are our “categories”. The links to our prior articles are saved under their appropriate categories. Would you please click on any category under “Post Archives” to read the titles of previous articles and click on the link of your interest to open the article.
Welcome to Our Financial Success Group!
To learn more tips on how to live below your income without sacrificing the quality of your life and start building wealth, would you please join our community for FREE by subscribing here:
https://ninasoap.com/membership-join/
Our Online Stores
Welcome to Nina’s Soap our Natural Products Store
Our Online Stores
Welcome to Nina’s Soap our Natural Products Store
Natural soaps are handmade with quality grade natural unrefined oils and butters, food grade sodium hydroxide, and herbs grown in our garden without pesticide or chemical fertilizer—- no additives, no fragrance, no dye.
Towels, washcloths, and cloth napkins are natural and eco-friendly alternatives of paper towels, paper napkins, and tissue papers for you to enjoy in the comfort of your home while saving money and the environment.
Best Seller: Nina’s Soap Flour Sack Individual Hand Towel – Set of 5: Small size cloth napkins to use as individual hand towels in the bathroom instead of paper towels or as napkin in the kitchen for family dinners:
https://ninassoap.com/product/ninas-soap-flour-sack-hand-towel-set-of-5/
Welcome to Liber Label our Apparel Store
Customs design clothing, home décor, accessories, and stationery with motivational quotes to lift your mood every day.
Business planner inserts, business tax checklist, to do list, many printable of our digital downloads can be purchased here and shipped directly to your door.
Welcome to LiberOutlet.com our Resale Store
New and used office supplies, toys, small kitchen appliances, household products, packaging supplies at a bargain price.
Welcome to Liberdownload.com, Digital Products Store
Budget and Monthly Expense Tracker, Checklist to create your online store, Inventory and Sales Excel Template…tools you need to manage your money, start and run your business successfully, and reach your financial success.
If you are a Sole Proprietor, a Limited Liability Company (LLC), an S Corporation, or an LLC taxed as an S Corporation, articles and videos on our channel would be helpful to file your business tax returns. If you need more help and would like to meet with us, would you check if our Group meeting session is the best fit for you.
Business Consulting Session: Virtual Group Meeting for new Business Owners that need help organizing their business income and expenses and be able to file business taxes themselves:
Small Business Group Session-Quarter 1:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/small-business-group-session-quarter-1/
Small Business Group Session-Quarter 2:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/small-business-group-session-quarter-2/
Small Business Group Session-Quarter 3:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/small-business-group-session-quarter-3/
Small Business Group Session-Quarter 4:
https://liberdownload.com/downloads/small-business-group-session-quarter-4/
Affiliate Links:
Bluehost: We host our websites at Bluehost and like their service. They take the time over the phone to help solve website issues
https://www.bluehost.com/track/ninasoap/
Please Register for Free
Registration
[/vc_wp_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]